
WHAT IS A STEM CELL, WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Stem cells are cells that can transform into many cell types when necessary. They work as an internal repair system in some organs and have the capacity to divide and multiply endlessly and transform into other cells. Stem cells can renew themselves by dividing and can also turn into certain cells that have functions for organs.
Common features of all stem cell types can be listed as follows.
-
Stem cells have the ability to divide and renew themselves. These reproductive cells can reproduce in millions within tissue or under laboratory conditions.
-
Stem cells are unspecialized cells, that is, they do not perform functions like cells in tissues and organs. The thing is, they do not function like a blood cell or a brain cell.
-
Stem cells can turn into specialized cells. When necessary, due to their own genetic effects or the influence of their microenvironment, stem cells transform into specialized brain, muscle, blood, intestinal epithelium, skin, cartilage and many other cell types and perform support, renewal and repair functions.
These properties of stem cells have led to their use in cellular treatments, this is called Cellular Regenerative Therapy.
Apart from these, stem cells are also distinguished from each other according to the period in which they are obtained from the body.
The cells obtained in the first week of fertilization in the first stages of life, before our tissues are formed, are called Embryogenic Stem Cells. These are Pluripotent cells, which means they have the ability to turn into all types of cells and tissues in the human body. Obtaining and using these cells and conducting research on them are subject to legal permissions.
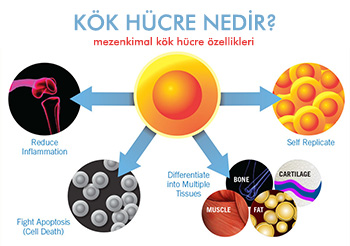
Adult stem cells are obtained from adult humans. They are multipotent cells, that is, they can transform into many cell types. Hemopoietic cells, that is, blood-forming stem cells, and Mesenchymal stem cells, that is, stem cells that make connective tissue, fat, muscle, bone and cartilage tissue cells, are in this class. They are found in various tissues in the body, and their use is not subject to legal permission.
Nowadays, transplantation of organs and tissues donated by other people instead of diseased or damaged organs and tissues is widely used. Studies to obtain healthy tissues or organs through stem cell studies continue scientifically. It is believed that organ transplants will be possible in the future without the need for organ donation. The repair of many organs that are injured or damaged due to disease can be achieved with new cell production, and therapeutic clinical studies on this subject have started in many centers.
For example, adult stem cells were injected directly into the heart muscle damaged as a result of infarction and it was observed that these formed new heart muscle cells. Similarly, bone marrow stromal stem cells administered intravenously were observed to increase vascularity in the damaged heart muscle. Just as stem cells turn into damaged dead cells, they also stimulate body repair mechanisms by secreting growth hormone and similar mediators.
Although adult stem cells were initially obtained mainly from bone marrow, recently they can be obtained from adipose tissue, nerve tissue, muscle and liver tissues. Among these tissues, fat tissue is preferred for obtaining stem cells because it is easily accessible, can be removed without harming the body, is abundant, contains more stem cells than other tissues, and does not require general anesthesia or hospitalization. The vascular stroma (cell community around the vessel) obtained from adipose tissue contains vascular-repairing cells, adipose tissue stem cells and 40% Mesenchymal Stem Cells. The amount of Mesenchymal stem cells in fat tissue is 500 times higher than in bone marrow.






